"The detection and grading of inflammation in rheumatology is made on the presence and amount of hyperemia inside, eg, the synovial membrane. There is, however, no definition of hyperemia, which on some US machines will be the mere presence of Doppler activity (relatively insensitive Doppler) and on others a qualitative assessment 'more than normal' when the Doppler has the ability also to detect flow in normal synovium. Even when using the same machine, different examiners may obtain different results (hyperemia versus no hyperemia) depending on how they adjust their Doppler, their scanning technique, and whether they fall into some of the pitfalls created by artifacts," warned Dr. Torp-Pedersen, from The Parker Institute at Fredericksberg Hospital in Copenhagen.
"Artifacts caused by physical limitations of the modality or inappropriate equipment settings may result in displayed flow conditions that may differ considerably from the actual physiologic situation. As a consequence, artifacts in Doppler imaging may be confusing and lead to misinterpretation of flow information," the authors write.
What is Doppler, anyway?
The Doppler effect detects a change in sound wavelength (frequency) caused by the motion of a sound source, receiver, or reflector. In medical US, the source and receiver are stationery and the Doppler effect is caused mainly by erythrocytes, which act as reflectors in motion. The difference between the frequency of the wave that was transmitted and the frequency of the wave received after bouncing off erythrocytes is the "Doppler shift." This shift has two parts. First, the sound wave is received by the moving erythrocytes; second, the sound wave is reflected toward the transducer (now functioning as a stationary receiver).
Color Doppler involves presenting flow information in color superimposed on the grey-scale Doppler image. The image displays the frequency shift for each "cell" of the Doppler color box as a color indicating the direction of flow: red for flow toward the transducer, blue for flow away from the transducer.
"The Doppler circuitry merely detects movements up and down in the image plane. A dark red spot may therefore be blood moving slowly directly towards the transducer or blood moving fast at an angle close to 90°.... In rheumatologic use, where the tortuous vessels are seen as color spots when they traverse the scanning plane, the so-called relative velocity information (different hues indicating different velocities) is not present," the authors explain.
Reverberation Artifact Showing Importance of Position of Color Box
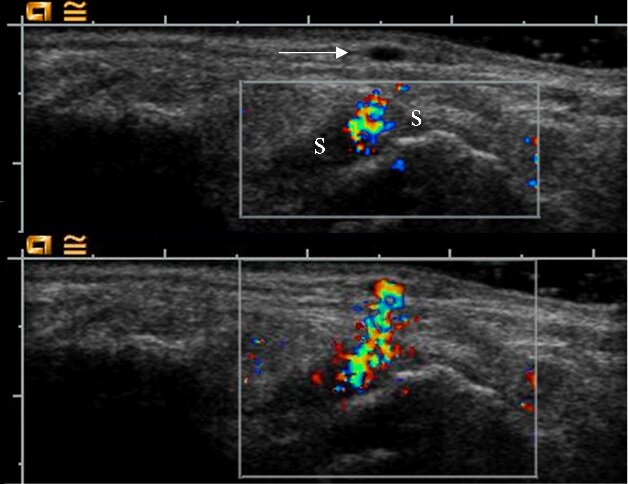
Superficial veins (arrow) are not included in the top image, in which the color box does not cover the most superficial part. Using that approach, the synovium (S) appears hyperemic. Extending the color box to the skin surface (bottom image) reveals that the color Doppler activity in the synovium is a reverberation artifact from the superficial veins.
Adapted from Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; doi:10.1136.ard.2007.078451.1
Power versus color
Power Doppler is theoretically more sensitive than color Doppler because it shows the power of the Doppler shift in each analysis cell rather than the mean frequency shift, but Dr. Torp-Pedersen said that power Doppler holds little advantage in rheumatology. "The issue when choosing Doppler modality in a rheumatologic setting is the sensitivity for flow. The theoretical advantage of power Doppler in sensitivity has disappeared in the newer high-end machines, where the trend is that color Doppler now is more sensitive than power Doppler. In less expensive equipment, power Doppler has the highest sensitivity."
Dr. Torp-Pedersen emphasized that whichever machine is used should be set for maximum power output. "A possible adverse effect of ultrasound in general and Doppler in particular is only an issue in prenatal ultrasound," he said.
Best Doppler settings
The specific recommendations include
- Doppler frequency: Optimum must be found in practice and not in theory. Lower frequency allows more penetration but produces a grainier image; higher frequency gives more detail of the vessels but less penetration.
- Color box: Make the box as small as possible and always let it go to the top of the image in order to be aware of reverberation artifacts.
- Pulse repetition frequency: Use a low frequency so the machine will apply the lowest possible filters and provide the highest sensitivity to flow.
- Color priority: Allows valid grey-scale information to override false Doppler information, such as motion artifacts in the tissue surround a pulsating artery, and allows valid Doppler information to override false grey-scale information. Set this function so that grey does not override color, because US in rheumatology is most often evaluating vessels that are not visible on grey scale.
- Filters: Set filters at their lowest setting.
- Gain: Turn up the Doppler gain until random noise is encountered, and then lower it until the noise disappears.
- Persistence: No advantage to high image persistence in rheumatology.
- Patient positioning: Patient must be comfortable with area to be examined completely relaxed so that tension in muscles and tendons does not produce movement artifacts. For hand or elbow scans, do not put the arm on the abdomen or thorax because breathing will produce movement artifacts.
- Examiner positioning: Arm used for scanning should be resting comfortably.
- Scanning technique: Use light pressure and a lot of visible scanning gel between the transducer and the skin. Pressure will decrease blood flow.
Potential pitfalls
Mirror images are one pitfall to watch out for when using Doppler imaging in rheumatology. "Any highly reflecting smooth surface may act as an acoustic mirror, and the Doppler image is just as prone to mirroring as the grey-scale image. In rheumatology, the mirrors will nearly always be bone surfaces.... Doppler mirror images will more or less always show false flow below a bone surface," Dr. Torp-Pedersen wrote.
Focusing is also a concern, since the Doppler is dependent on focus positioning. If the focal point in longitudinal studies is not consistently in the area under investigation, "substantial differences may be falsely generated or falsely overlooked."
The authors emphasize the importance of using the same settings from patient to patient or from visit to visit if US is being used to compare patients or to monitor response to therapy. Readings are also reliable only if they are from the same make and model of US machine.
"Much of the variation in the literature concerning detection of hyperemia, detection of normal flow, or presence or absence of increased flow after contrast injection may be attributed to differences in machinery," they conclude.
Best Settings for Doppler Ultrasound in Rheumatology
| Parameter | Setting |
| Doppler Frequency | Lowest or highest, depending on machine |
| Pulse Repetition Frequency | Lowest possible without motion artifacts |
| Color Priority | Color |
| Wall Filter | Lowest possible without motion artifacts |
| Persistence | Lowest |
| Gain | On the threshold to noise |
| Focus | Where the highest sensitivity is required |
Adapted from Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; doi:10.1136.ard.2007.078451.1
Reference






